Heart Development
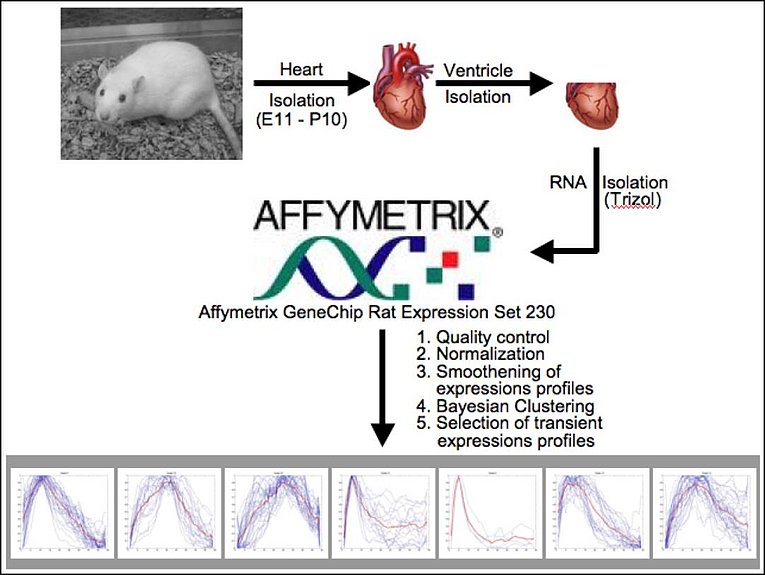
Congenital heart disease is the most common type of birth defect, with six to eight out of every 1,000 live birth being affected. Half of them will require immediate surgery after birth, while the other 50% will require surgery or medication during their childhood. Defects in cardiac valves are the most common type of congenital malformations, accounting for 25% to 30% of all cardiovascular anomalies. Based on our temporal resolved RNA expression analysis and morphological association studies we could recently predict Nephronectin as a new regulator of cardiac valve development and Gpr126 of trabeculation. As the cause for most congenital heart diseases are still unknown it is our goal to continue with the identification of novel regulators of heart development.